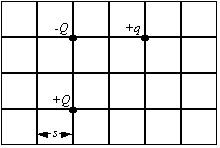
Q- Five 1 inch square plates are arranged as shown in figure. The plate spacings are 0.01 inch. The arrangement is to be used for a displacement transducer by observing the change in capacitance with the distance x. Calculate the sensitivity of the device in picofarads per inch. Assume that the plat…
Solution Search
. : "Electrostatics"
Electric Potential
Q- Ohmic heating raises the temperature of a tungsten filament to the point that electrons begin to "boil" off. A high voltage power supply establishes an accelerating potential difference of 900 V between the filament and a circular metal disk located 2.0cm away. The disk diameter is 1.0cm. Assumin…
Electrostatics: Coulomb's Law
Q- Two positive, 1 nC charges are located on the x-axis. Charge Q1 is located at the origin and charge Q2 is located at (4,0) which is 4 cm from the origin.
(a) Calculate the magnitude and direction of the force experienced by Q2 due to Q1.
(b) A third charge Q3 of 2 nC is positioned on the y-ax…
Electrostatics: Dielectric and Polarization
Q- Two parallel conducting plates are separated by distance d and the potential difference between them is V. A dielectric slab of dielectric constant k and uniform thickness nearly d is inserted between the plates. As the dielectric slab is not smooth enough, it touches the plates in some regions a…
Electrostatics: Coulomb's Law
Q- Two equally charged point mass of mass m each are suspended from a point by massless threads of length L. In equilibrium position each thread makes and angle ɵ with vertical.
(a) Find the ratio of magnitudes of horizontal electric force and vertical gravitational force on a the masses.
(b) Wh…
Electrostatics
(On request - Nshwah)
Q- Two charges are placed between the plates of a parallel plate capacitor. One charge is +q1 and the other is q2 = +6.58 mC. charge per unit are on each plate has a magnitude of σ = 1.39*10-4 C/m2. If the magnitude of force on q1 due to q2 is equal to that on q1 due to the …
Electric Flux
(On request - Nshwah)
Q- Figure shows top view of two surfaces intersecting at right angle. Surface 1 has an area of 1.5 m2 and that of the surface 2 is 3.3 m2. Uniform electric field E of strength 270 N/C is making angle 35o with surface 2. Find electric flux through
(a) Surface 1
(b) Surface 2
…Electrostatics: Field in Cavity
Q. A sphere of radius r0 carries a volume charge density ρE. A spherical cavity of radius r0/2 is then scooped out and left empty, as shown.
(a) What is the magnitude and direction of the electric field at point A?
(b) What is the direction and magnitude of the electric field at point B? Poin…
Capacitors
Q- Two capacitors are connected to a battery with a two way swatch, as shown in figure. The capacitors are initially uncharged. When the switch is thrown to the left the capacitor C1 = 10 µF is charged to 50 V. Now the switch is thrown to the right and the voltage across C1 is drops to 35 V.
(a)…
Coulomb's Law: Force and Field
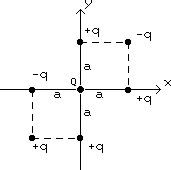
Q- Four charges q1 = q3 = - q and q2 = q4 = + q, where q = 7 µC, are fixed at the corners of a square with sides a = 2.2 m, as in figure.
(a) Calculate the x- and y-components of the net electric field at the midpoint M of the bottom side of the square.
(b) Find the total force exerted on q4 by…
Electrostatics: Field and Force
Q- Throughout space there is a uniform electric field in the - y direction of strength E = 550 N/C. There is no gravity. At t = 0, a particle with mass m = 2 g charge q = -11 µC is at the origin moving with a velocity v0 = 45 m/sat an angle q = 25° above the x-axis.
(a) What is the magnitude of …
Coulomb's Law: Force and Field
Q- Two charges placed on the x axis. Qa = 4 µC at x = 0 and Qb = - 4 µC at x = 22cm.
(a) Find the net electric field at point P at x = - 6 cm.
(b) Find the force on Qb due to Qa .
(c) The charges Qa and Qb are now attached to the ends of a spring whose un-stretched length is s0 = 22 cm and…

Comments